Home » MedECC reports » Special Report Interlinking climate change with the Water – Energy – Food – Ecosystems (WEFE) nexus in the Mediterranean Basin » Chapter 2. Drivers of change and their impacts on WEFE in the Mediterranean region
Special Report Interlinking climate change with the Water - Energy - Food - Ecosystems (WEFE) nexus in the Mediterranean Basin
Chapter 2. Drivers of change and their impacts on WEFE in the Mediterranean region
Executive Summary
The Mediterranean region faces a variety of drivers of change that operate at different spatial scales. These include climate change, land use changes, habitat alterations, air, soil and water pollution, population growth, industrialisation, urbanisation, lifestyle changes and conflicts (war). These drivers collectively impact the region's ecological and societal dynamics, including all the components of the WEFE nexus. Since the WEFE components follow complex hierarchical links and feedback, changes in one component can have cascading effects on other interconnected components, creating a complex web of interactions. To reduce the negative impacts of the drivers of change, the interlinkages among the WEFE components must be thoroughly evaluated at local scale, under a holistic view, to enable better-informed decisions and effective and more robust management policies. This chapter underscores the importance of recognising the interconnectedness of water, energy, food, and ecosystems in the Mediterranean region and the need for comprehensive assessment and management strategies to address the challenges posed by external environmental and social stressors.
Water security in the Mediterranean faces a multifaceted challenge stemming from a blend of factors, such as climate change, rapid population expansion in urban areas, unsustainable resource management and land use, and agricultural practices. The impacts of the drivers of change have negative effects on the availability and quality of water resources, but this effect will cascade, through a series of interactions, on the other components of the WEFE nexus, including crop yield reductions, alterations of agricultural commodity prices, reduction of electricity production and generation efficiency, desertification, habitat loss, and affecting vulnerable species.
Climate change, pollution, changes in diets, population growth, and urbanisation are interconnected and contribute to the emergence of vulnerabilities through impacts on food availability, access and quality. There are substantial differences in terms of food security between Southern Europe and North Africa. Business as usual responses to address food security related challenges through industrialisation can lead to adverse effects on other WEFE components, such as increased soil and water pollution and GHG emissions, degradation of underground water resources, salinisation, loss of agrobiodiversity, and increase of energy demand and further greenhouse gas emissions.
The energy security of the Mediterranean region is significantly affected by a multitude of challenges from both the offer and demand sides. The escalating energy demands in the Mediterranean region are attributed to population growth, urbanisation and industrialisation. Moreover, addressing energy inequality is essential, as certain population segments have abundant energy access while others face deprivation. The dependence of the area on power generation methods that require significant amounts of water exposes them to the risk of decreased water availability and difficulties in managing water resources, due to the effects of climate change and the competition with other sectors. Similarly, competition for other resources to produce solar or wind energy, such as land for agricultural purposes and ecosystem services, further exacerbates the complex interplay within the nexus framework, showing the need to promote holistic analyses to address such challenge.
The pressures exerted on Mediterranean ecosystems impact their health resulting in ecosystem degradation, loss of biodiversity among others. These modifications disrupt the provision of multiple ecosystem services (namely, provisioning, regulating, and cultural) which subsequently have direct impacts on WEFE components as well as further cascading effects on other components of the WEFE.
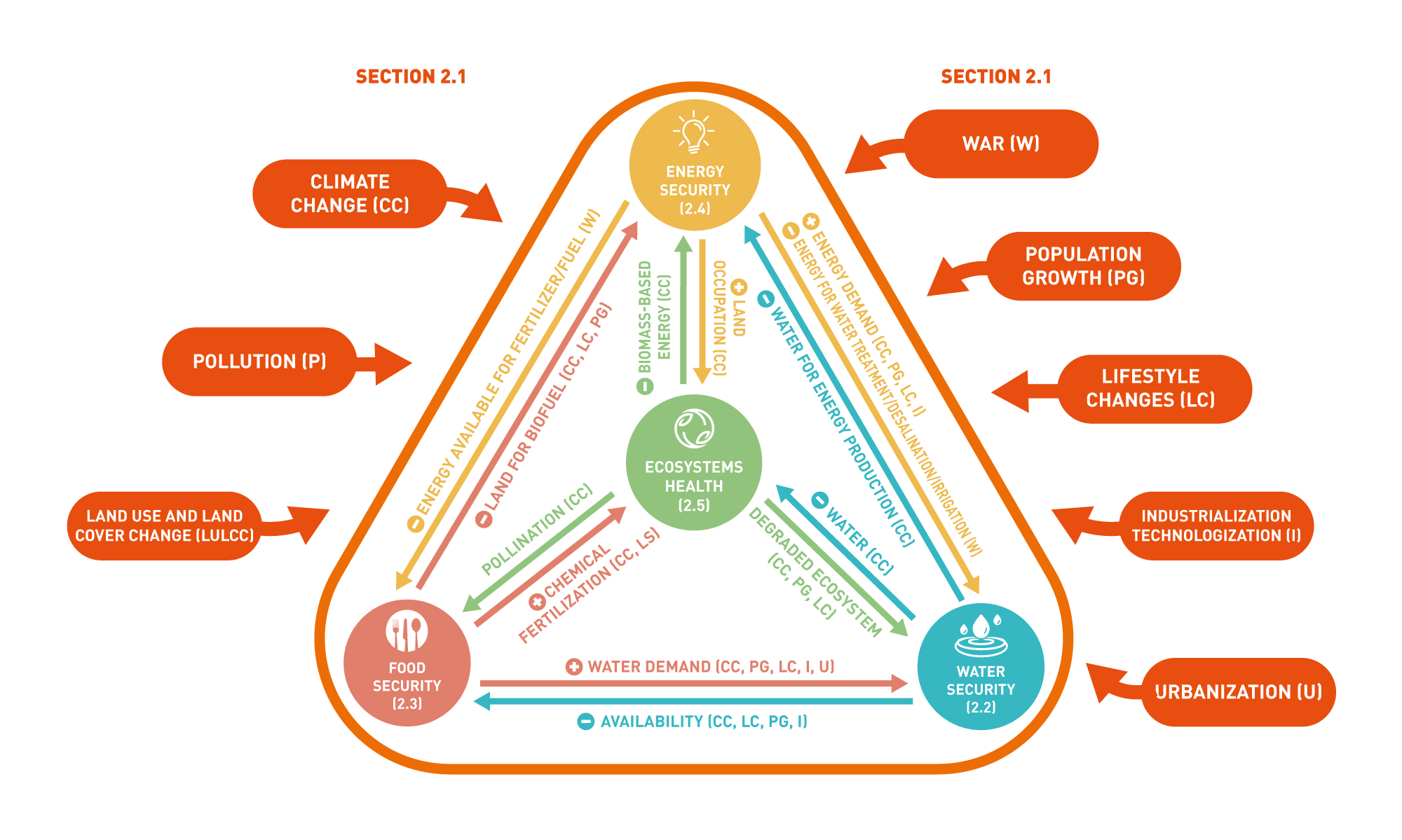
Figure 2.3 | Schematic figure of the rationale of Chapter 2.
How to cite the report
Contributors
Coordinating Lead Authors

Margarita
Garcia-Vila
Institute for Sustainable Agriculture, Centre of the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) / Spain
hide

Marta Guadalupe
Rivera Ferre
INGENIO (CSIC-UPV) / Spain
hide

Tarik
Chfadi
Mohammed VI Polytechnic University / Morocco
hide

Ahmed
El Kenawy
Instituto Pirenaico de Ecologia, CSIC, Spain / Spain
hide
Lead Authors

Cristina
Branquinho
University of Lisbon / Portugal
hide

Jorge
Lorenzo-Lacruz
University of La Rioja / Spain
hide

Emanuela
Menichetti
Mediterranean Energy Observatory (OME), France/Italy / France/Italy
hide

Safwan
Mohammed
University of Debrecen / Hungary
hide
/ Syria
hide

Alberto
Sanz-Cobena
Universidad Politécnica de Madrid / Spain
hide
Contributing Authors

Sofia
Augusto
University of Porto / Portugal
hide
Jordi
Badosa
Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique - Ecole Polytechnique / France
hide
Francisco Javier
Bonet García
University of Córdoba / Spain
hide

Philippe
Drobinski
Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique / Institut Pierre Simon Laplace & Energy4Climate Interdisciplinary Center / France
hide
Houda
Ghazi
Cadi Ayyad University / Morocco
hide

Hicham
Mastouri
Mohammed VI Polytechnic University / Morocco
hide

Lia
Rapella
LMD-IPSL, Ecole Polytechnique, Institut Polytechnique de Paris, CNRS / France
hide

Helena Cristina
Serrano
Center for Ecology, Evolution and Environmental Changes (CE3C), CIÊNCIAS ULISBOA / Portugal
hide