Home » MedECC reports » Special Report Interlinking climate change with the Water – Energy – Food – Ecosystems (WEFE) nexus in the Mediterranean Basin » Chapter 3. WEFE nexus in support of adaptation and mitigation
Special Report Interlinking climate change with the Water - Energy - Food - Ecosystems (WEFE) nexus in the Mediterranean Basin
Chapter 3. WEFE nexus in support of adaptation and mitigation
Executive Summary
In addressing adaptation and/or mitigation strategies in the Mediterranean region, a focus on achieving multiple goals across the water, energy, ecosystems and food sectors is imperative. Identifying synergies between these aspects is crucial to avoid negative outcomes and trade-offs. An integrated approach to the Water-Energy-Food-Ecosystem (WEFE) nexus is necessary, one which takes into account its interconnected nature and the potential for rebound effects from addressing individual aspects separately. Because of the region's temporal and spatial variabilities, dealing with the WEFE nexus requires transdisciplinary approaches that incorporate social, political, and governance aspects. In cases of high expected impacts from climate change, transformative adaptation involving significant changes in human inputs and system reorganisation becomes necessary, as incremental adaptations may reach their limits in effectiveness. Watershed management serves as an effective unit for managing the nexus, especially given the Mediterranean region's vulnerability to water stress. The complexity of the region's socio-economic and political diversity necessitates transboundary strategies in adaptation and mitigation efforts, alongside global agreements as a complement to the Paris Agreement. Evaluating adaptation and mitigation strategies in a context-specific manner is essential to ensure effectiveness. While digital and technological solutions, early warning tools, and climate services are valuable, they must be integrated with nature-based solutions, and broad societal understanding and engagement are vital. Despite being solutions, improvements in irrigation techniques can lead to unintended consequences on the WEFE nexus, such as increased water use through the expansion of irrigated surface area and intensity. Embracing behavioural changes, such as reducing meat consumption and food waste, and encouraging restrained consumption and sufficiency, holds high potential for both adaptation and mitigation in the face of environmental challenges.
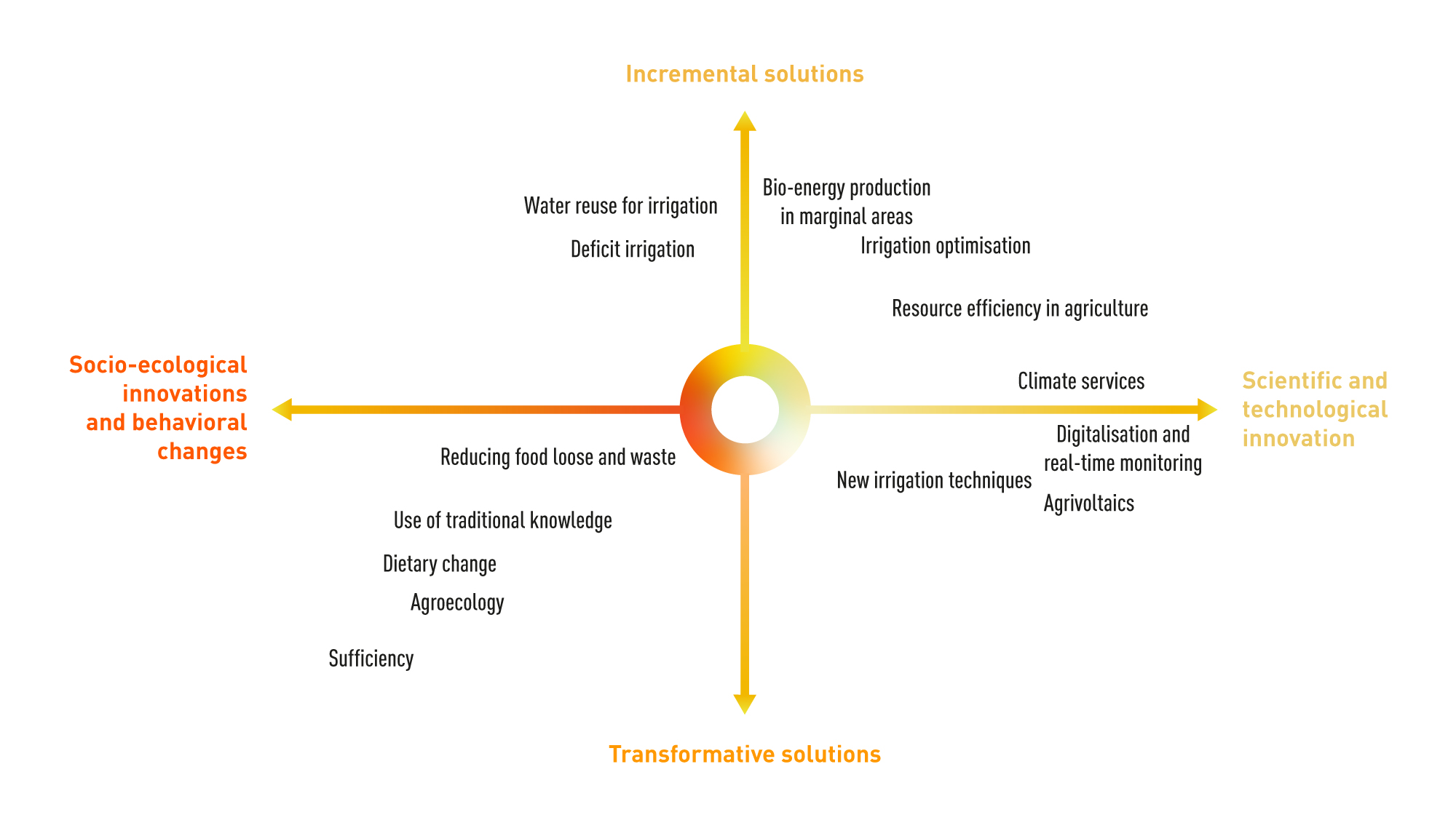
Figure 3.1 | Different gradients of possible adaptation and mitigation solutions for WEFE components used around the Mediterranean region. Adaptation and mitigation solutions range from incremental to transformative, and from socio-ecological innovations and behavioural change to scientific and technological innovation.
How to cite the report
Contributors
Coordinating Lead Authors
Lead Authors

Eduardo
Aguilera
CEIGRAM, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid / Spain
hide

Youssef
Brouziyne
International Water Management Institute (IWMI) / Morocco
hide

Insaf
Mekki
National Research Institute for Rural Engineering, Water and Forestry / Tunisia
hide

Marta
Terrado
Barcelona Supercomputing Center (BSC-CNS) / Spain
hide

George N.
Zaimes
Laboratoty of Geomorphology, Edaphology and Riparian Areas (GERi Lab)s, International Hellenic University / Greece
hide
Contributing Authors
Nassim
Ait-Mouheb
National Research Institute for Agriculture, Food and Environment (INRAE) / France
hide
Jordi
Badosa
Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique - Ecole Polytechnique / France
hide

Philippe
Drobinski
Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique / Institut Pierre Simon Laplace & Energy4Climate Interdisciplinary Center / France
hide

Jerome
El Jeitani
University of Florence / Italy/Lebanon
hide

Nina
Graveline
National Research Institute for Agriculture, Food and Environment (INRAE) / France
hide

Flavio
Lupia
CREA - Research Center for Agricultural Policies and Bioeconomy / Italy
hide

Hicham
Mastouri
Mohammed VI Polytechnic University / Morocco
hide

Tiziana
Pirelli
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Global Bioenergy Partnership (GBEP) / Italy
hide

Giuseppe
Pulighe
CREA - Research Center for Agricultural Policies and Bioeconomy / Italy
hide

Marta Guadalupe
Rivera Ferre
INGENIO (CSIC-UPV) / Spain
hide




